I am embarking on a series of articles that will
cover LAN technologies over the course of the next year or so.
My goal is to make this series a form of tutorial that can be
compiled into an introduction guide to LANs.
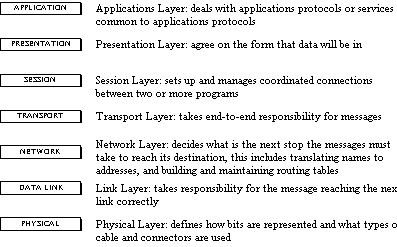
The series will follow the OSI Model, as defined
by the ISO and including IEEE specifications. Although the chart
depicts a top down view of operation, the technologies are discussed
from the bottom up, as each subsequent layer builds on the previous
layer.

The first area of discussion is the physical medium
in which all the LAN data is transported - the cable. Cabling
for LANs has evolved over the course of 24 years, from coax to
fiber optics, with every imaginable option and type available.
Today the predominate cable type used is ANSI/TIA/EIA
568A - UTP Category (Cat) 5. This cable has four twisted pair
conductors, and can support frequencies up to 350Mhz (at least
so far) and transmission data rates of up to 1Gb (in trial at
1Gb). Depending on the topology type either two pairs or all four
pairs may be used, and also pin-outs vary depending on topology.
The predominant connector used is an RJ-45, 8 pin/8 conductor
jack/outlet.
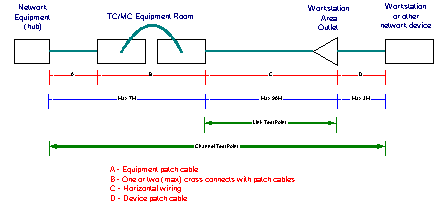
For most LAN topologies, the ANSI/TIA/EIA 568A specifications
for Cat 5 allow for a total end-to-end distance of 100M. This
is broken down into 90M for the horizontal (or main) run (MC/TC
to WAO), 7M for the interconnection to the active electronics
(in the MC/TC) and 3M for the connection of the device (usually
the workstation) to the WAO.
Under the ANSI/TIA/EIA 586A specs, there are two
supported pin-out configurations: T568A and T568B
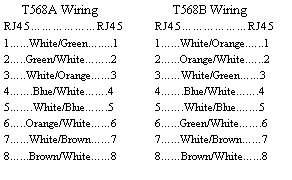
Although the differences between T568A and B are
subtle, if they are mixed within a cable plant most topologies
will not operate when the pairs are "crossed". When
installing a new cable plant, if the ANSI/TIA/EIA 586A spec is
not included detailing T568A or B, T568A is the default. However
I have seen many more new and upgraded cable plants installations
using T568B.
The pinouts used for Ethernet and Token Ring are as follows:
Ethernet: pins 1,2 and 3,6
Token Ring : pins 4,5 and 3,6
I have also seen many cable plant installations where
only the specific pins required for the topology were connected/terminated,
thus allowing for either a duplex RJ-45 WAO to use a single cable
run, or the extra conductors at the end of the cable were simply
cut off. This does not follow the ANSI/TIA/EIA 586A specs, nor
does it allow for some of the newer topologies to be used on the
existing Cat 5 cable plant. Therefore, in order to be fully compliant
with the ANSI/TIA/EIA 586A specs and allow for future topologies
to be implemented, all 8 conductors must be terminated per the
ANSI/TIA/EIA 586A specs, following either the T568A or B guidelines.
Glossary:
568A - ANSI/TIA/EIA Commercial Telecommunications Standard
ANSI - American National Standards Institute
EIA - Electronics Industries Association
ISO - International Standards Organization
MC - main cross connect room
OSI - Open System Interconnect
TC - terminal cross connect room
TIA - Telecommunications Industry Association
UTP - unshielded twisted pair
WAO - work station area outlet
In the next article I'll discuss the active electronics
that the cabling connects to….hubs.
Copyright © 1997 Jeffrey L. Carrell. All Rights
Reserved
Have a question or want to know more details about
e-mail, the Internet, electronic communications or related technologies?
Send me a note and I'll
try to discuss
it in a future article. If your company or organization
would like an Internet or Networking presentation let me know. (no commercial
pitch)